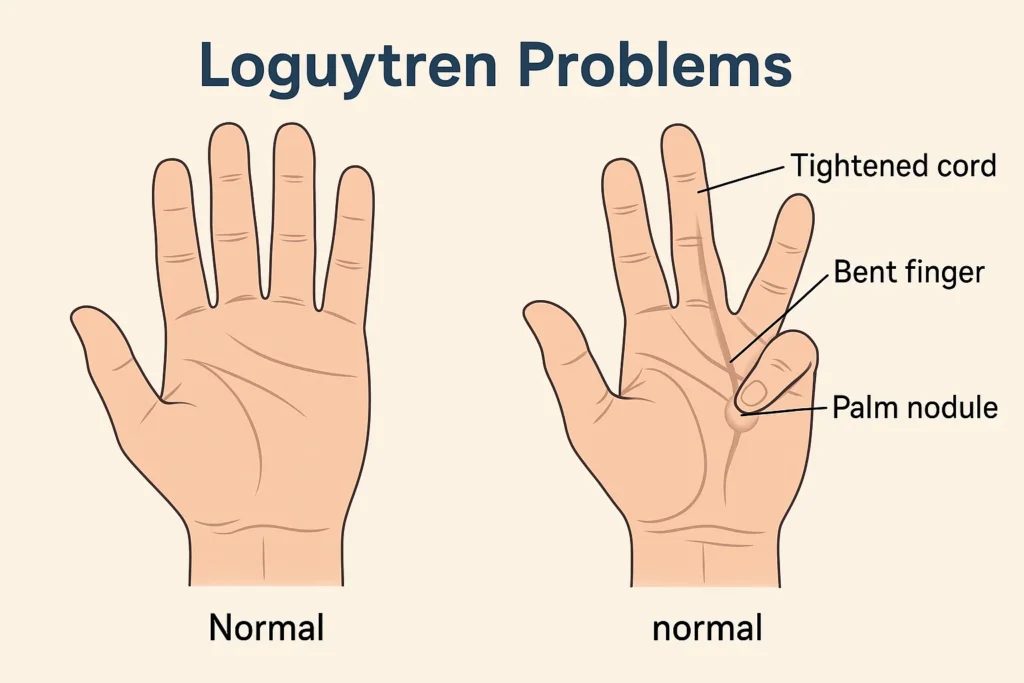
Loguytren problems, medically known as Dupuytren’s Contracture, occur when the connective tissue beneath the skin of the palm thickens, gradually pulling one or more fingers into a bent position. While not typically painful, it can severely limit hand function over time.
Let’s dive into everything you need to know — symptoms, causes, treatment options, expert insights, and what’s new in 2025.
What Is Dupuytren’s Contracture (Loguytren Problems)?
Dupuytren’s Contracture is a progressive hand condition that starts with small nodules in the palm and may lead to permanent finger contractures. It commonly affects the ring and little fingers and can occur in one or both hands.
Key Characteristics:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Palmar Nodules | Hard lumps develop beneath the skin on the palm. |
| Cord Formation | Thick cords develop and extend into the fingers. |
| Contracture | Fingers bend toward the palm and lose flexibility. |
| Grip Issues | Difficulty placing the hand flat or grasping objects. |
What are loguytren problems?
Loguytren problems refer to Dupuytren’s Contracture, a hand disorder causing the fingers to bend toward the palm due to thickened connective tissue. It worsens over time and limits hand mobility.
Early Signs and Symptoms
The condition progresses gradually, often unnoticed until it begins to impact daily tasks.
Common Symptoms:
- A firm, painless lump in the palm
- Tightening of skin over the lump
- Fingers slowly curling toward the palm
- Inability to place the hand flat on a surface (positive tabletop test)
- Difficulty shaking hands or putting on gloves
Causes and Risk Factors
While the precise cause remains unclear, research shows a combination of genetic and environmental triggers. Here’s what science says in 2025:
Primary Risk Factors:
- Genetics: A family history increases the chance of developing the condition.
- Age: Most common in people over 50.
- Gender: Males are 7x more likely to develop severe forms.
- Ethnicity: Predominantly affects individuals of Northern European descent.
- Lifestyle: Smoking and heavy alcohol use are linked to faster progression.
- Chronic Illnesses: Diabetes and epilepsy are associated with higher risk.
How Loguytren Problems Are Diagnosed
Doctors can typically diagnose Dupuytren’s based on a physical exam. Imaging is rarely needed unless the presentation is unusual.
Diagnosis Includes:
- Palpation: Feeling for lumps or cords in the palm.
- Tabletop Test: Patient attempts to lay hand flat on a surface.
- Functional Assessment: Evaluating hand mobility and grip strength.
Current Treatment Options (Updated for 2025)
Treatment varies based on severity. In 2025, less invasive procedures are gaining traction for early intervention.
1. Non-Surgical Treatments
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Observation | Mild cases may not need treatment. Regular check-ins recommended. |
| Collagenase Injections | FDA-approved enzyme injections break down the cords. Now more refined with better recovery. |
| Needle Aponeurotomy | Minimally invasive technique to puncture and break cords. Quick recovery and minimal scarring. |
| Stretching & Splints | Often prescribed by hand therapists to delay progression. |
2. Surgical Options
| Procedure | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Fasciotomy | Cuts the affected tissue to release tension. |
| Fasciectomy | Removal of diseased fascia; used for moderate to severe cases. |
| Dermofasciectomy | Used when the condition recurs; involves skin grafting. |
Note: Surgery is typically reserved for advanced stages or when hand function is significantly impaired.
Latest Insights from 2025
- Biologic Therapies: Clinical trials are underway to use stem cells to regenerate damaged connective tissue.
- 3D Imaging for Planning: Precision-based hand mapping before treatment is becoming standard.
- AI-Powered Monitoring: Mobile apps now assist with early detection and progression tracking.
Expert Advice on Managing Loguytren Problems
According to Dr. Anna Meier, a hand surgeon at Cleveland Clinic:
“Early intervention can make a big difference. The sooner we start therapies like injections or needling, the better the long-term hand function outcomes.”
Lifestyle Tips for Better Hand Function
- Stretch Daily: Gentle hand stretches improve blood flow and delay stiffness.
- Limit Alcohol & Smoking: Both are linked to faster disease progression.
- Protect Your Hands: Avoid repetitive grip-heavy tasks that strain tendons.
- See a Hand Therapist: Regular therapy maintains flexibility and strength.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Dupuytren’s Contracture painful?
Most cases are not painful, especially in early stages. Some may experience mild discomfort.
Can I prevent loguytren problems?
While you can’t fully prevent it, reducing risk factors like smoking and managing diabetes may slow progression.
How long does recovery take after surgery?
Recovery varies. Minor procedures like needling take 1–2 weeks, while full surgery can take 6–8 weeks.
Does Dupuytren’s Contracture recur after treatment?
Yes, recurrence is possible, especially if only cords are cut and not removed.
Final Thoughts
Loguytren problems may start small but can have a major impact if left untreated. Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms early, and seeking timely care can help you maintain function and quality of life.
Whether you’re in the early stages or exploring advanced treatment options in 2025, there’s hope and help available.
This comprehensive video provides an overview of Dupuytren’s Contracture, discussing its symptoms, underlying causes, and available treatment options.
Note: This content is provided for educational purposes and is not intended as medical guidance. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.