Great Potential in Small Things: The Latest Developments in 3D Printing

In recent years, 3D printing has transitioned from a niche technology predominantly used for prototyping and experimental purposes to a robust and mature industrial process. As this transformation continues, the latest developments highlight how 3D printing is revolutionizing various fields, particularly in medical and pharmaceutical applications, while also reshaping industrial manufacturing. This evolution has significant implications for the financial prospects of the 3D printing industry.
3D Printing in Microfluidic Testing: A Medical and Pharmaceutical Revolution
One of the most exciting advancements in 3D printing is its application in microfluidic testing—a crucial component in medical diagnostics and pharmaceutical research. Microfluidic devices manage small fluid volumes with high precision and are essential for experiments involving blood tests, chemical reactions, and drug development. Traditionally, manufacturing these devices involved complex and expensive processes, limiting their accessibility and scalability.
3D printing microfluidic devices has emerged as a game-changer in this arena. By using 3D printing technologies, researchers and manufacturers can produce microfluidic devices with intricate designs and high precision at a fraction of the cost and time required by traditional methods. For example, the ability to rapidly prototype and iterate on designs allows for quicker development cycles, leading to faster advancements in diagnostic tools and drug testing.
Recent developments have seen the integration of advanced materials such as biocompatible resins and thermoplastics, which enhance the performance and applicability of 3D-printed microfluidic devices. Additionally, innovations in printing technology, such as multi-material and high-resolution printers, enable the creation of complex microfluidic channels and structures that were previously unattainable.
This capability not only accelerates research and development but also opens new possibilities for personalized medicine and tailored therapeutic solutions. As the demand for rapid and precise diagnostic tools grows, 3D printing positions itself as a critical technology in the future of healthcare and pharmaceuticals.
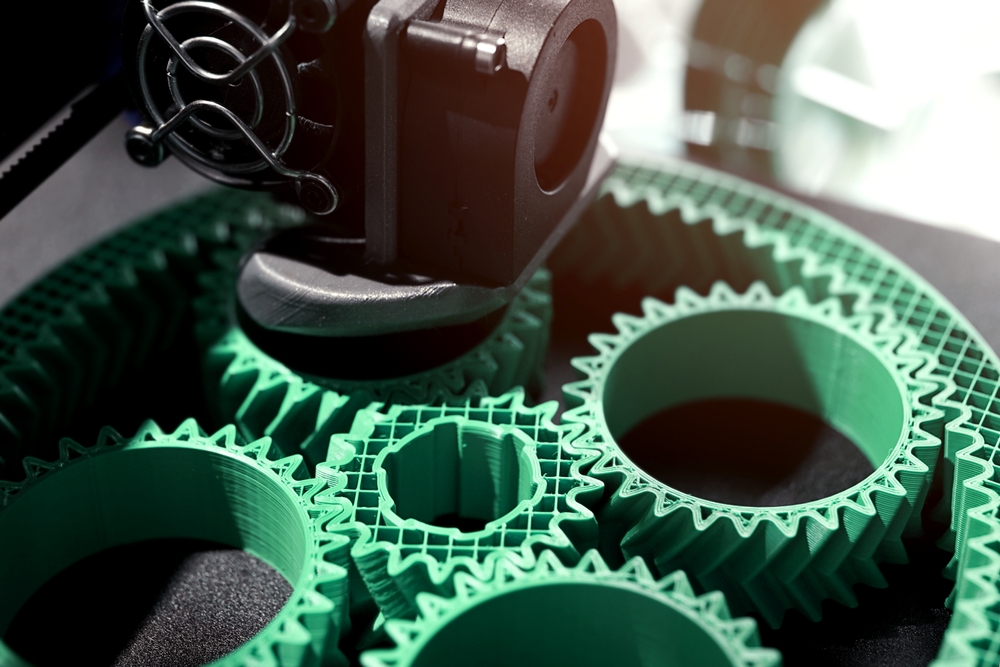

From Prototyping to Production
Beyond medical applications, 3D printing is steadily transitioning from a prototyping tool to a full-fledged industrial production technology. The industry’s evolution reflects broader trends in manufacturing, where additive manufacturing (AM) is becoming integral to various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods.
Several key factors are driving this shift:
Material Advancements: The development of new materials, including high-strength composites and metal alloys, has significantly expanded the range of applications for 3D printing. These materials offer properties such as durability and thermal resistance, making 3D-printed parts viable for end-use applications.
Speed and Scale: Improvements in printing speed and scalability have made it possible to produce larger quantities of high-quality parts. Advanced 3D printers can now produce complex geometries and large-scale components more efficiently, catering to industrial needs.
Cost Reduction: The costs associated with 3D printing are decreasing as technology matures and becomes more widely adopted. Economies of scale and advancements in printer technologies are driving down the costs of both the equipment and materials used in 3D printing.
Customization and On-Demand Production: One of the most significant advantages of 3D printing is its ability to create customized and on-demand products. This capability is transforming supply chains and manufacturing processes, enabling just-in-time production and reducing inventory costs.
Financial Implications and Industry Outlook
The financial implications of these developments are substantial. As 3D printing technology continues to evolve and find applications beyond prototyping, it presents significant opportunities for growth and investment.
The 3D printing industry is projected to experience robust growth. According to various market research reports, the global market for 3D printing equipment alone is expected to expand from around $13 billion in 2023 to over $30 billion by 2028. By 2030 3D printing as a whole is expected to be a $118 billion industry. This growth is driven by increased adoption across multiple industries and ongoing technological advancements.
Investors are increasingly recognizing the potential of 3D printing. Companies specializing in advanced 3D printing technologies, materials, and applications are attracting significant investment. Venture capital and private equity funds are keen to support innovative startups and established firms that are pushing the boundaries of what 3D printing can achieve.
For industrial manufacturers, the transition to 3D printing offers considerable cost savings. The ability to streamline production processes, reduce material waste, and minimize inventory costs enhances profitability and operational efficiency.
Disruption of Traditional Supply Chains: 3D printing’s ability to produce parts on-demand and locally disrupts traditional supply chains. This shift reduces the reliance on global manufacturing hubs and offers more resilient and adaptable production solutions.
Summary
The latest developments in 3D printing underscore its transformative impact across medical, pharmaceutical, and industrial sectors. By enabling rapid prototyping, advancing microfluidic testing, and transitioning to industrial-scale production, 3D printing is not only enhancing technological capabilities but also driving substantial economic growth. As the industry continues to mature, it presents promising financial opportunities for investors and manufacturers alike, marking a new era of innovation and efficiency in production and design.